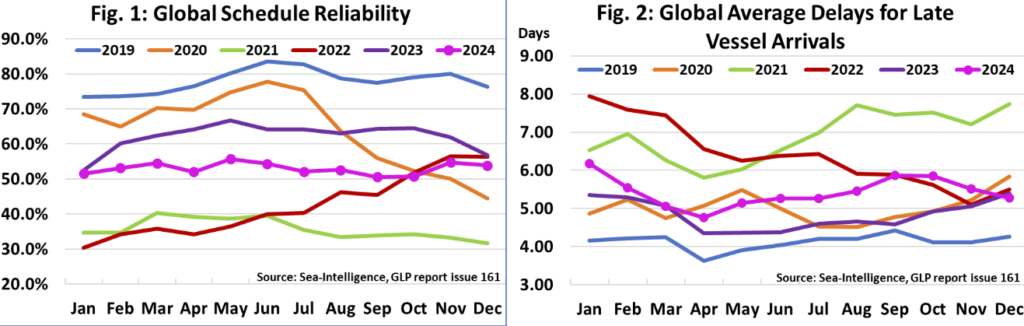
Global schedule reliability decreased by 0.9 percentage points month on month (MoM) to 53.8 per cent in December 2024.
Sea-Intelligence has published issue 161 of the Global Liner Performance (GLP) report, with covers schedule reliability through 2024.
This detailed analysis looks into reliability in 34 trade channels and over 60 carriers. The following is a summary of the report’s key global results.
READ: Global schedule reliability reaches highest 2024 figure
Throughout 2024, schedule reliability has stayed primarily between 50 per cent and 55 per cent. In December 2024, schedule reliability was 3.0 percentage points lower than it was in the previous year, noted Sea-Intelligence.
The average delay for LATE vessel arrivals declined by 0.23 days MoM to 5.28 days, the lowest since July 2024. On a year-over-year (YoY) basis, the December 2024 value was 0.12 days lower.
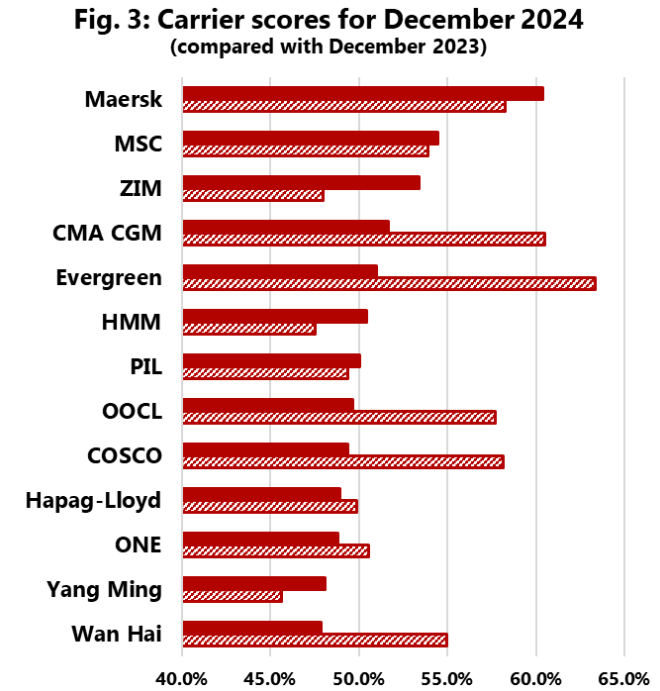
Maersk was the most reliable of the top 13 carriers in December 2024, with schedule reliability of 60.4 per cent.
There were six carriers with schedule reliability ranging from 50 per cent to 60 per cent, with the remaining six carriers falling within a tight range of 47 per cent to 50 per cent.
According to Sea-Intelligence’s findings, Wan Hai was the least reliable with 47.9 per cent schedule reliability. In December 2024, the difference between the most and least trustworthy carriers was less than 13 percentage points.
Only four of the top 13 global carriers improved schedule reliability on a MoM basis, with ZIM experiencing the highest rise of 6.0 percentage points.
On a YoY basis, just six carriers improved, while Evergreen was the only carrier to decrease by double digits.
In October 2024, global schedule reliability increased by 0.9 percentage points MoM to 51.5 per cent.